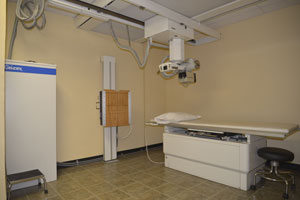
X-RAYS
X-radiation (composed of X-rays) is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz (3×1016 Hz to 3×1019 Hz) and energies in the range 100 eV to 100 keV.
However, much higher-energy X-rays can be generated for medical and industrial uses, for example radiotherapy, which utilizes linear accelerators to generate X-rays in the ranges of 6-20 MeV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to with terms meaning Röntgen radiation, after Wilhelm Röntgen, who is usually credited as its discoverer, and who had named it X-radiation to signify an unknown type of radiation. Spelling of X-ray(s) in the English language includes the variants x-ray(s) and X ray(s).
X-rays with photon energies above 5-10 keV (below 0.2-0.1 nm wavelength) are called hard X-rays, while those with lower energy are called soft X-rays. Due to their penetrating ability hard X-rays are widely used to image the inside of objects, e.g. in medical radiography and airport security. As a result, the term X-ray is metonymically used to refer to a radiographic image produced using this method, in addition to the method itself. Since the wavelengths of hard X-rays are similar to the size of atoms they are also useful for determining crystal structures by X-ray crystallography. By contrast, soft X-rays are easily absorbed in air and the attenuation length of 600 eV (~2 nm) X-rays in water is less than 1 micrometer.
The distinction between X-rays and gamma rays is not universal; however, it is common practice to see the two types of radiation separated by their origin: X-rays are emitted by electrons, while gamma rays are emitted by the atomic nucleus. An alternative method for distinguishing between X- and gamma radiation is on the basis of wavelength, with radiation shorter than some arbitrary wavelength, such as 10−11 m, defined as gamma rays.[10] These definitions usually coincide since the electromagnetic radiation emitted by X-ray tubes generally has a longer wavelength and lower photon energy than the radiation emitted by radioactive nuclei.
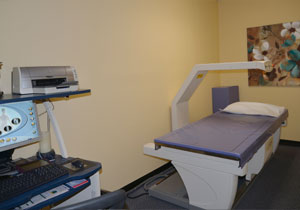
BONE DENSITY
Bone density (or bone mineral density) is a medical term normally referring to the amount of mineral matter per square centimeter of bones.Bone density (or BMD) is used in clinical medicine as an indirect indicator of osteporosis and fracture risk.
This medical bone density is not the true physical "density" of the bone, which would be computed as mass per volume.
It is measured by a procedure called densitometry, often performed in the radiology or nuclear medicine departments of hospitals or clinics.
The measurement is painless and non-invasive and involves low radiation exposure. Measurements are most commonly made over the lumbar spine and over the upper part of the hip.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI),
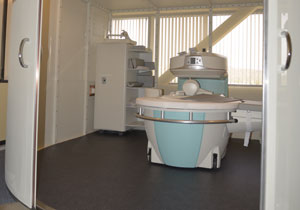
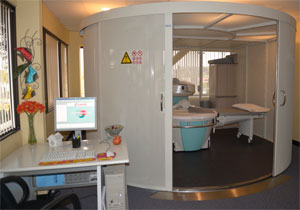
Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI), or magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to investigate the anatomy and function of the body in both health and disease. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields and radiowaves to form images of the body. The technique is widely used in hospitals for medical diagnosis, staging of disease and for follow-up without exposure to ionizing radiation.
MRI has a wide range of applications in medical diagnosis and there are estimated to be over 25,000 scanners in use worldwide. MRI has an impact on diagnosis and treatment in many specialties although the effect on improved health outcomes is uncertain. Since MRI does not use any ionizing radiation its use is recommended in preference to CT when either modality could yield the same information. MRI is in general a safe technique but the number of incidents causing patient harm have risen.
to MRI include most cochlear implants and cardiac pacemakers, shrapnel and metallic foreign bodies in the orbits, and some ferromagnetic surgical implants. The safety of MRI during the first trimester of pregnancy is uncertain, but it may be preferable to alternative options. The sustained increase in demand within the healthcare industry for MRI has led to concerns about cost effectiveness and overdiagnosis.